All microphones work in a comparable approach. They’ve a diaphragm (or a ribbon) that strikes in response to adjustments in air strain attributable to sound waves impinging on the diaphragm – equally to how the diaphragm or ‘eardrum’ within the human ear responds to sound.
The motion of this diaphragm, or ribbon, then produces a altering voltage, with a optimistic worth (or amplitude) when the diaphragm strikes a method and a destructive worth (or amplitude) when the diaphragm strikes the alternative approach. There are three predominant sorts of microphone to select from – dynamic, ribbon, and condenser.
Dynamic mics
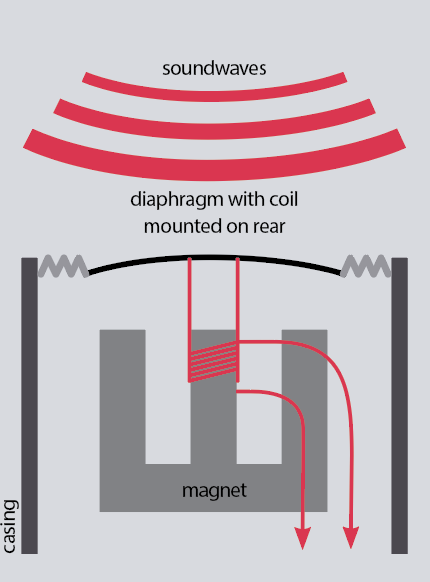
With a so-called ‘dynamic’ microphone (the phrase ‘dynamic’ means altering or transferring), a small coil of wire, positioned inside the magnetic discipline of a everlasting magnet, is connected to the diaphragm. When a sound wave enters the microphone, the diaphragm vibrates forwards and backwards in a similar technique to the actions of the sound wave.
When a wire strikes in a magnetic discipline, a present is induced in it. So, the strain of the sound wave vibrates the diaphragm, which in flip strikes the coil within the magnetic discipline, inducing {the electrical} sign within the wire, which is then handed to the microphone cable (typically by a step-up transformer to enhance the voltage).
The mass of the diaphragm and coil association implies that the transferring coil mic suffers from inertia points. That’s, the association is proof against adjustments in its state of movement, which means that it doesn’t totally precisely characterize the sound strain, significantly at excessive frequencies the place the diaphragm and coil association should change velocity and course extra continuously.
As one thing of a aspect observe, chances are you’ll discover that the development of a transferring coil mic is similar to that of a loudspeaker driver, which consists of a loosely suspended cone connected to a transferring voice coil in shut proximity to a set magnet. The speaker driver works within the reverse technique to the microphone – the circulate of a sign by the coil induces a magnetic discipline which drives the coil away from the magnet, transferring the speaker cone. That is the rationale {that a} speaker driver could also be wired as much as an enter and used as a rudimentary mic.
Ribbon mics
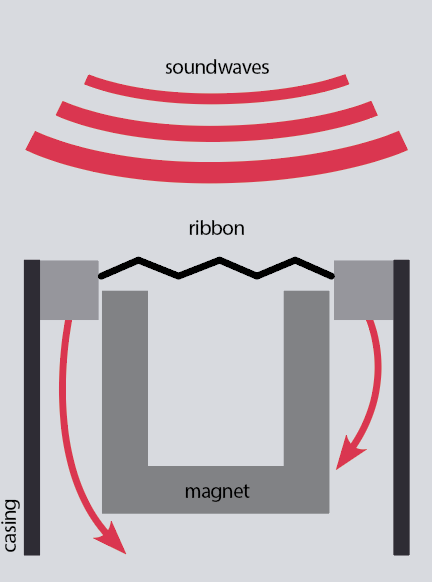
Ribbon mics are one other type of dynamic mic, though normally billed as a definite design by producers attributable to their high-end desirability.
Within the case of a ribbon microphone, the ribbon is product of metallic and is suspended in a magnetic discipline, so when it vibrates, various electrical indicators are produced. The output voltage of the ribbon is low, so most ribbon mics additionally include a step-up transformer to spice up the voltage to an optimum stage. The lighter association of the transferring elements helps to beat a number of the inertia issues of the transferring coil mic, which means that ribbon mics are usually extra correct at increased frequencies than transferring coil.
Ribbon mics are typically extra delicate than transferring coil mics, so are higher suited to studio work than stay efficiency.
Condenser mics
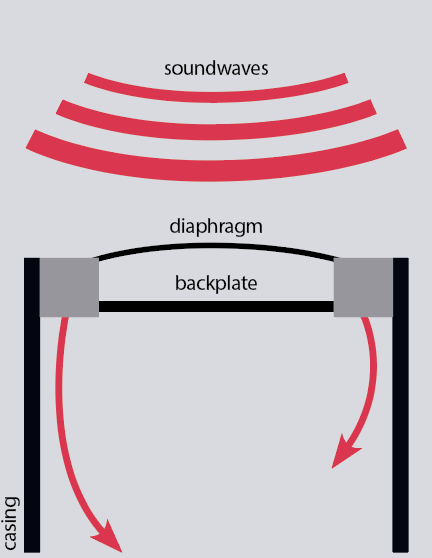
Condenser mics don’t function utilizing the identical primary magnetic ideas as dynamic mics, as an alternative being based mostly round a smaller, capacitor-based ingredient.
In a condenser microphone, the diaphragm acts as one plate of a capacitor, and the vibrations produce adjustments within the distance between the plates. These adjustments are translated into various electrical indicators by considered one of two strategies – DC‑biasing or RF biasing.
As a result of the entrance plate of a condenser mic is considerably smaller than the diaphragm and coil/ribbon setup of a dynamic mic, it’s lighter and due to this fact its velocity and course of motion adjustments extra quickly, permitting it to create a extra correct illustration of the sound strain.
As such, condenser mics normally have a extra correct frequency response curve than dynamic mics. Electret mics are a type of condenser mic the place the capacitor dielectric is completely charged with out the necessity for phantom energy. The electret itself is a small capacitor which features in a broadly comparable technique to a standard condenser mic.
Pickup (polar) patterns
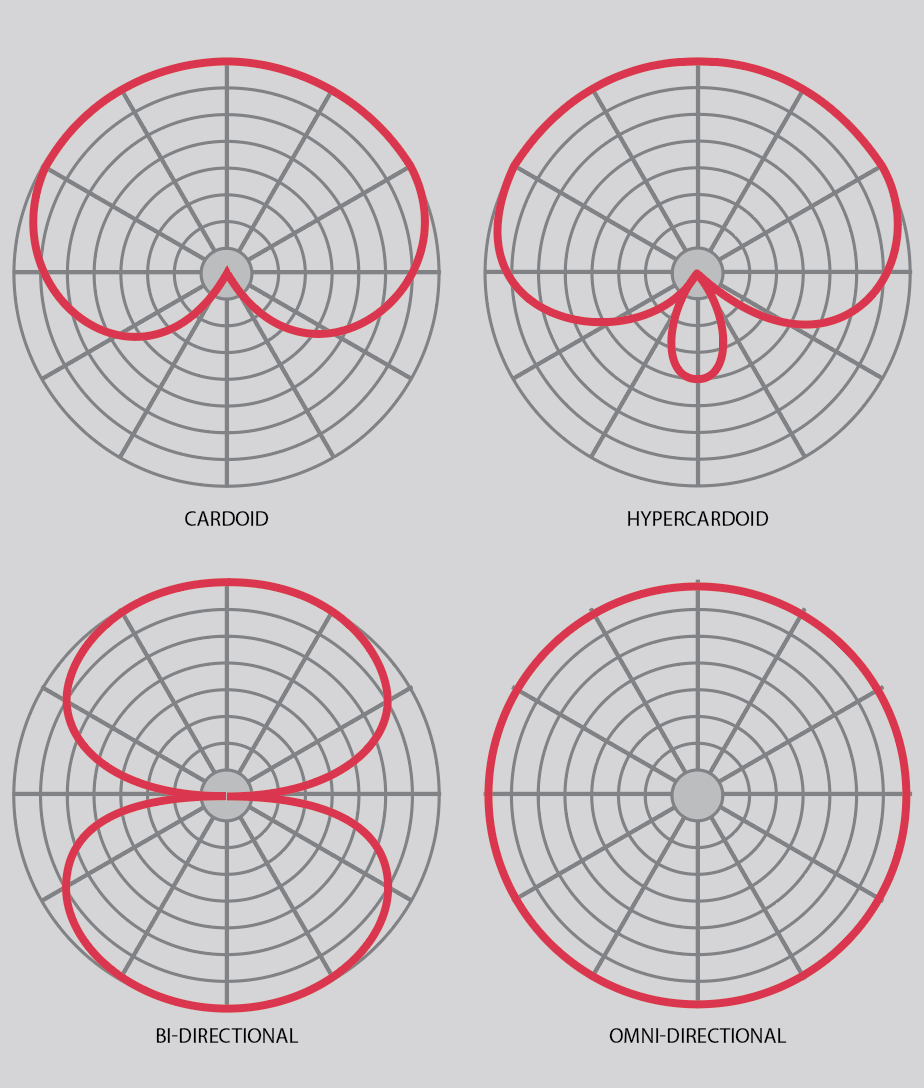
One other typical microphone specification is the pickup sample, extra normally known as a polar sample. This can be a round graph displaying how the microphone picks up sound coming from the totally different instructions in a circle across the microphone.
An omni-directional microphone, as its identify suggests, picks up sound equally from all instructions. That is significantly helpful if you wish to seize the atmosphere of the house across the microphone.
A cardioid microphone, once more as its identify suggests (cardioid means heart-shaped), picks up sounds in a heart-shaped sample, primarily from the entrance, whereas rejecting sounds coming from the perimeters and the rear. The benefit right here is that this microphone principally simply captures sound from the sound supply that it is pointing at.
A hyper-cardioid is comparable however with a narrower space of sensitivity at the entrance and a small space of sensitivity on the rear. A variation on that is the hypercardioid, which has a good narrower pickup space on the entrance and even much less pickup from the rear. These pickup patterns will help isolate the devices that they’re meant to choose up extra successfully, and likewise assist to minimise suggestions in stay conditions.
The opposite predominant kind of pickup sample is the figure-of-eight or bi-directional sample, wherein sound is picked up equally from the entrance and the rear, whereas sound from the perimeters is strongly rejected. Microphones with this sort of pickup sample can be utilized to file two close by sound sources, both aspect of the microphone, whereas rejecting sounds coming from the opposite two instructions.
Want-to-know specs

Essentially the most primary measurement of a mic’s efficiency is its frequency response. A frequency response curve reveals how the microphone’s response successfully boosts and cuts explicit frequencies of the sound it’s trying to choose up.
It may appear logical {that a} mic with a wonderfully flat frequency response could be essentially the most fascinating. Generally, this can be a pretty good guideline, however a fast take a look at the frequency response of the previous trustworthy Shure SM58 shortly demonstrates the truth that a mic with an apparently inaccurate frequency response can nonetheless be an trade commonplace.
Along with frequency response curves and primary polar patterns, any good producer can even publish numerous different specs for his or her microphones. These can vary from the fundamentals like impedance to a mics’ ranges of self-noise, most sound strain stage and sensitivity, which supplies you a clue as to how a lot achieve you’ll want out of your preamp.
