Lily Katz / Android Authority
When the MP3 participant took off within the late Nineteen Nineties, the format itself entered the general public consciousness in a manner not many others have — with maybe the Phrase doc being an exception. However what’s an audio format, anyway, and why do you have to care?
This information will cowl among the hottest codecs that audio streaming companies use at this time and clarify their variations.
What’s an audio file format?
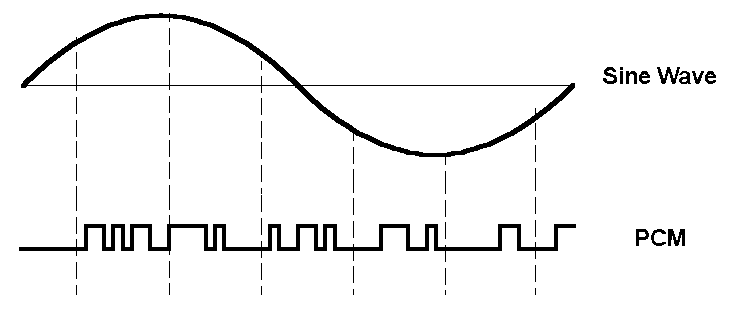
A digital audio file is how recorded content material will get saved on a pc, media participant, smartphone, or different gadget. Digital audio is, at its most simple stage, a sequence of numbers {that a} gadget can use to recreate sound waves. There are numerous methods to perform this after which compress (or not) the ensuing information. We all know that by sampling a sound wave within the course of from analog to digital conversion with at the least 16 bits at 44.1kHz that we are able to completely reproduce the captured sign once more in a while. That is because of some math referred to as the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem. We are able to obtain larger bitrates and frequency ranges, however whether or not anybody can hear a distinction — although the perfect headphones — is debatable at finest.
If we simply save that information as is (often called pulse code modulation or PCM), the file takes up numerous area. That’s why each lossy and lossless types of audio compression have been developed. Lossy audio throws out audio frequencies our ears can’t hear, whereas lossless preserves all of them. Lossy audio codecs may use different tips to compress audio even additional, which we’ll cowl just a little later.
As a result of most individuals lately entry their music by way of streaming companies, compressed, lossy file codecs are the predominant manner content material will get distributed. That’s superb in case you’re casually listening, however some individuals demand the utmost high quality. Consequently, an rising variety of high-quality and even lossless streaming choices at the moment are obtainable. However there’s no getting round the truth that lossy codecs take up much less area and eat up much less cell information, because the chart beneath makes clear.
| Stereo file sizes (16-bit 44.1kHZ) | WAV | AIFF | FLAC (typical) | MP3 (320Kbps) | MP3 (192Kbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stereo file sizes (16-bit 44.1kHZ)
1 min |
WAV
10.6 MB |
AIFF
10.6 MB |
FLAC (typical)
6.4 MB |
MP3 (320Kbps)
2.4 MB |
MP3 (192Kbps)
1.4 MB |
| Stereo file sizes (16-bit 44.1kHZ)
4 minutes |
WAV
41.6 MB |
AIFF
41.6 MB |
FLAC (typical)
24.9 MB |
MP3 (320Kbps)
9.6 MB |
MP3 (192Kbps)
5.6 MB |
| Stereo file sizes (16-bit 44.1kHZ)
1 hour |
WAV
635 MB |
AIFF
635 MB |
FLAC (typical)
381 MB |
MP3 (320Kbps)
144 MB |
MP3 (192Kbps)
84 MB |
MP3

The MP3 audio file format as soon as reigned supreme when it got here to downloading music. The truth is, the format is so synonymous with cell music options that “MP3 participant” is now generic for an audio-playing gadget. Nonetheless, lately it’s much less outstanding for a wide range of causes. It’s nonetheless hanging on, although. Understanding MP3 information might help us perceive different codecs extra simply as properly, so we’ll begin right here.
An MP3 file is a lossy audio file, that means it discards information our ears can’t hear. Virtually each human has a listening to vary someplace within the vary of 2oHz to 20kHz. The higher restrict decreases with age, however on the whole, that’s the vary inside each noise you’ll ever hear lies. As a result of we all know different frequencies are subsequently superfluous, MP3 discards all frequencies outdoors this vary.
To additional avoid wasting area, MP3 information use much more tips. Audio engineers use noise-shaping algorithms primarily based on the psychoacoustic results of the human ear and mind to take away elements of music that we shouldn’t be capable of hear. For instance, the mind can’t differentiate between two frequencies proper subsequent to one another. Moreover, the grownup human ear struggles to determine the path of high-frequency sounds. It additionally begins to lose sensitivity above 16kHz. Plus, loud sounds can masks quieter ones. All these might be eliminated with little to no noticeable distinction to the tip listener.
Mainly, MP3 information take away frequencies we can’t hear and frequencies we may hear in isolation, however can’t due to the best way they’re mixed in a specific tune.
An MP3 splits up a observe into 576 pattern frames, and Quick Fourier Transforms (FFT) are used to acquire frequency information from these frames. The frequency information is then analyzed to see if any alternatives exist to use the compression guidelines primarily based on human listening to as described above. In that case, these parts are rounded down (quantized) to decrease bitrates, which helps save area. Information on restoring every body to its full sound wave illustration will get saved to a 32-bit header.
The bitrate determines the utmost allowed file dimension for every body. The extra aggressive the compression, the extra probably the algorithm removes one thing audible. Moreover, such a filtering and chopping isn’t excellent, and the quantization can go away behind artifacts that some individuals can hear. This lossy psychoacoustic compression is then adopted up by a lossless Huffman coding compression that’s much like .zip file to avoid wasting extra space.
If that sounds too sophisticated, the takeaway is that MP3 information take away frequencies we can’t hear and ones we theoretically may hear in isolation, however can’t in a specific tune because of auditory masking. This could result in fairly small file sizes. Whether it is achieved too aggressively or with a bitrate that’s too low, although, high quality can undergo. Consequently, MP3 isn’t all too common anymore for streaming.
AAC, M4A, and OGG Vorbis audio codecs

Zak Khan / Android Authority
Audio compression can take many types, and different codecs have been developed. These use barely completely different algorithms and strategies to perform the duty, so we are able to’t evaluate them primarily based on bitrate alone.
OGG Vorbis is an open-source different to MP3. It nonetheless makes use of FFT and comparable strategies to research and quantize mask-able frequency info however employs a special algorithm. Vorbis additionally takes the noise ground under consideration to enhance low bitrate efficiency. Spotify makes use of this format at 320kbps.
There’s additionally AAC, which is utilized by Apple Music, TIDAL, Pandora, and YouTube Music. It’s an evolution of the MPEG (MP3) format and permits for larger pattern charges as much as 96kHz. Plus, it could actually dynamically change body lengths between 1024/960 or 128/120 samples for higher decision when required. It performs higher at decrease file sizes than MP3s, as well.
One other file sort you would possibly encounter is the M4A file. These information are encoded utilizing the AAC format, after which saved in an MPEG-4 container, therefore the file extension .m4a. Apple created this kind as a response to MP3. Whereas not fairly as universally supported, it isn’t uncommon.
For these causes, you may’t instantly evaluate bitrates and declare a better bitrate can be a better-sounding file between AAC and MP3, as an example. Decrease bitrate AAC and M4A information can nonetheless sound good whereas taking on much less area.
That makes codecs like OGG Vorbis and AAC interesting for streaming companies. They will ship higher-quality sound whereas consuming much less of your cell information.
FLAC
For those who don’t wish to throw out any frequencies however nonetheless need a file that’s smaller than uncooked information, that’s the place FLAC is available in. FLAC doesn’t discard any a part of a recording, and subsequently it’s referred to as lossless. Apple’s model of a lossless codec is named ALAC. Each of those codecs operate quite like a .zip file. For those who’ve ever zipped and unzipped a set of information, you’ll perceive the essential concept. Nothing will get eliminated. The FLAC file simply appears to be like for tactics to consolidate repeating patterns and information, that are then reconstructed upon playback.
Nonetheless, FLAC information won’t ever be as small as MP3 or AAC information. However as bandwidth will get cheaper and extra accessible, extra streaming companies supply the power to stream utilizing FLAC. These are sometimes “HD,” “Extremely HD,” or “HiFi” subscriptions. Amazon Music, TIDAL HiFi and HiFi Plus, Deezer Premium, and Qobuz supply FLAC streaming.
Remember that FLAC information are bigger than lossy codecs and may devour a lot of your information. For those who save them to a tool, they’ll additionally begin taking on space for storing fairly shortly.
WAV and AIFF audio codecs
Audio recordings might be simply pure PCM saved to a tool, which is basically what WAV (on Home windows) and AIFF (on Mac) are. They signify among the earliest types of storing digital music. These information haven’t any compression or anything utilized to them. The truth is, you could find out their file dimension fairly simply with the next equation:
PCM Measurement = pattern price X (bits per pattern /8) X time in seconds X variety of channels
Consequently, these codecs can result in extremely giant file sizes. Which means they’re quite uncommon for streaming and downloading, though companies like HDtracks do supply them. What these information are actually helpful for is audio mixing and enhancing. As a result of no conversion, compression, or anything has occurred, it’s straightforward and fast to edit tracks, save them, after which edit them once more as required.
FAQs
WAV information are uncompressed and retain all unique information, which is nice for post-production work. The downside is that the file sizes are so giant. FLAC information supply lossless audio high quality too, however they’re compressed, in order that they take up much less room in your media participant.
The main audio codecs are uncompressed (WAV, AIFF), lossless compressed (FLAC, ALAC), and lossy compressed (Opus, MP3, AAC).
Spotify lest artists add audio information as FLAC or WAV codecs, and listeners can stream Ogg/Vorbis at 96/160/320kbps.



